Worse COVID during 3Q pregnancy if 2.5 ng lower Vitamin D – meta-analysis
Serum vitamin D levels and COVID-19 during pregnancy: A systematic review and meta- analysis
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN, September 2022, DOI: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2022.09.008
Sadegh Mazaheri-Tehrani, Mohammad Hossein Mirzapour, Maryam Yazdi, Mohammad Fakhrolmobasheri, Amir Parsa Abhari IRAN

This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Background: Serum vitamin D level is reported to be associated with the risk of incidence, and severity of COVID-19 in the general population. During pregnancy, immune system alterations in line with changes in vitamin D metabolism may affect the course of COVID-19. Thus, we aimed to systematically review the association between vitamin D, pregnancy, and COVID-19.
Methods: A systematic literature search was conducted in PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Embase, and Google Scholar until the end of May 2022. Mean differences (MD) with 95% CI were used as desired effect sizes to assess the association of serum vitamin D levels with risk of incidence and severity of COVID-19 in pregnant women.
Results: Among 259 records, 7 and 6 studies were included in the systematic review and metaanalysis, respectively. All included studies had acceptable quality. Our results demonstrated an insignificant difference between infected women and non-infected controls (MD =-2.55 ng/ml, 95% CI: -6.85 - 1.74). But serum vitamin D levels in severe/moderate cases compared to mild ones (MD=-2.71 ng/ml, 95% CI: -4.16 - -1.25) is significantly lower.
Conclusion: Based on the current evidence, serum vitamin D level does not associate with risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection among pregnant women, but we find a significant association with the severity the of disease. These findings may be helpful in similar conditions and future studies to better understand the complex immune alterations during pregnancy.
📄 Download the PDF from Researchgate via VitaminDWiki
VitaminDWiki - studies in both categories Virus and Pregnancy
This list is automatically updated
{category}
VitaminDWiki – COVID-19 treated by Vitamin D - studies, reports, videos
{include}
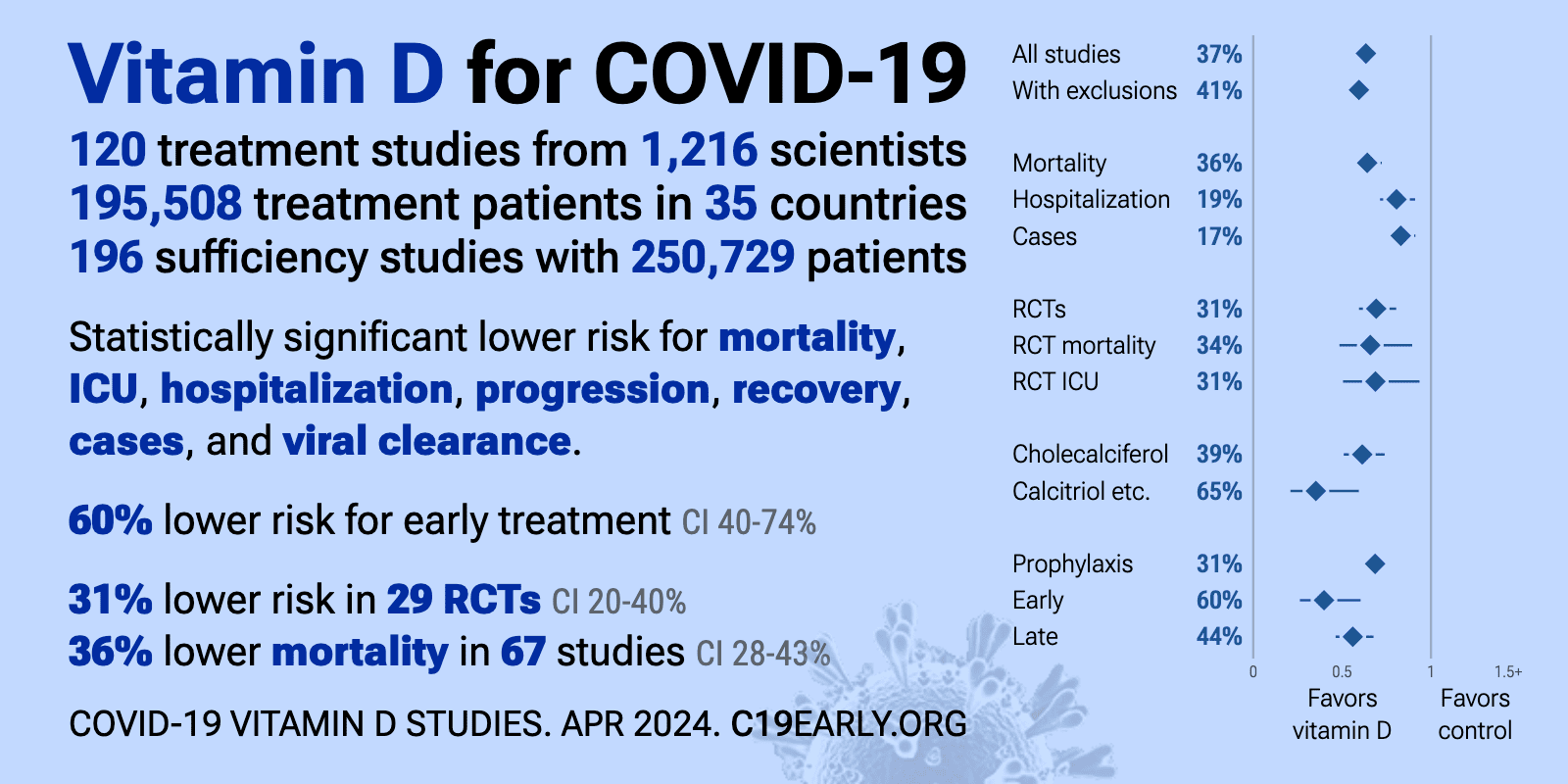
- The above image is automatically updated
VitaminDWiki – 26 health factors increase the risk of COVID-19 – all are proxies for low vitamin D includes pregnancy
{include}
