Many viral diseases can be fought by immune system-augmented Vitamin D - Sunil
Unlocking insights: Navigating COVID-19 challenges and Emulating future pandemic Resilience strategies with strengthening natural immunity
Heliyon 2024 Jul 17;10(15):e34691. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34691
Sunil J. Wimalawansa
Table of Contents

Those with more vaccinations were more likely to get COVID infection

Death rates in countries with more >70% vaccinated were100X higher than counries with <15% vaccinated

Cost of material to prevent a COVID death

The original COVID-19 vaccines, developed against SARS-CoV-2, initially mitigated hospitalizations. Bivalent vaccine boosters were used widely during 2022-23, but the outbreaks persisted. Despite this, hospitalizations, mortality, and outbreaks involving dominant mutants like Alpha and Delta increased during winters when the population’s vitamin D levels were at their lowest.
Notably, 75 % of human immune cell/system functions, including post-vaccination adaptive immunity, rely on adequate circulatory vitamin D levels.
Consequently, hypovitaminosis compromises innate and adaptive immune responses, heightening susceptibility to infections and complications. COVID-19 vaccines primarily target SARS-CoV-2 Spike proteins, thus offering only a limited protection through antibodies. mRNA vaccines, such as those for COVID-19, fail to generate secretory/mucosal immunity-like IgG responses, rendering them ineffective in halting viral spread. Additionally, mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 binding domain reduce immune recognition by vaccine-derived antibodies, leading to immune evasion by mutant viruses like Omicron variants. Meanwhile, the repeated administration of bivalent boosters intended to enhance efficacy resulted in the immunoparesis of recipients. As a result, relying solely on vaccines for outbreak prevention, it became less effective. Dominant variants exhibit increased affinity to angiotensin-converting enzyme receptor-2, enhancing infectivity but reducing virulence. Meanwhile, spike protein-related viral mutations do not impact the potency of widely available, repurposed early therapies, like vitamin D and ivermectin. With the re-emergence of COVID-19 and impending coronaviral pandemics, regulators and health organizations should proactively consider approval and strategic use of cost-effective adjunct therapies mentioned above to counter the loss of vaccine efficacy against emerging variants and novel coronaviruses and eliminate vaccine- and anti-viral agents-related serious adverse effects. Timely implementation of these strategies could reduce morbidity, mortality, and healthcare costs and provide a rational approach to address future epidemics and pandemics. This perspective critically reviews relevant literature, providing insights, justifications, and viewpoints into how the scientific community and health authorities can leverage this knowledge cost-effectively.
📄 Download the PDF from VitaminDWiki
Conclusions
The original COVID-19 vaccines effectively reduced hospitalizations but faced major challenges during winter outbreaks, leading to increased hospitalizations and mortality. Adequate vitamin D is critical for most human immune functions, including post-vaccination adaptive immunity. Individuals with low 25(OH)D concentrations have compromised immune systems and have less robust immune responses after vaccination, increasing their susceptibility to infections. Besides, COVID-19 mRNA vaccines predominantly target SARS-CoV-2 Spike proteins, providing limited antibody protection.
Moreover, mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines provide no mucosal immunity, thus failing to prevent virus transmission. Additionally, mutations in the receptor binding regions of the SARS-CoV-2 viruses allow Omicron mutants to evade immune detection by antibodies. Besides, repeated bivalent vaccine boosters weaken the immune system and increase vulnerability to infection and re-infection. Consequently, exclusive reliance on COVID-19 vaccines to control outbreaks became ineffective. In contrast, Spike protein mutations do not impact the efficacy of repurposed, already approved generic, widely available early therapies like vitamin D and ivermectin, thus remain effective. Regulators should consider approving them as cost-effective adjunct therapies, and health organizations should make them available to address emerging variants and enhance vaccine efficacy in future epidemics and pandemics. Timely implementation of the actions mentioned above has the potential to reduce morbidity, mortality, and healthcare costs, providing a rational, cost-effective approach without serious adverse effects of medications for future outbreaks and pandemics.
Summarized by Perplexity AI Dec 2024
This comprehensive research article examines the challenges and limitations of COVID-19 vaccines while exploring alternative strategies for pandemic management. Here are the key points:
Vaccine Limitations and Challenges
Efficacy Issues
Original COVID-19 vaccines initially reduced hospitalizations but failed to prevent viral transmission
mRNA vaccines did not generate mucosal immunity, allowing continued viral spread
Vaccine effectiveness declined significantly against new variants, dropping below 40% for bivalent boosters
Viral Mutations
Omicron variants developed multiple mutations in receptor binding domains
New variants showed increased infectivity but reduced lethality
Mutations enabled immune evasion against vaccine-derived antibodies
Alternative Approaches
Vitamin D Role
75% of immune cell functions depend on adequate vitamin D levels
Vitamin D deficiency compromises both innate and adaptive immunity
Winter outbreaks correlate with seasonal drops in population vitamin D levels
Cost-Effective Treatments
Vitamin D and ivermectin emerged as highly cost-effective interventions
Treatment costs per life saved:
Vitamin D: $11
Ivermectin: $25
Compared to thousands for newer antivirals
Future Recommendations
Strategic Changes
Need for broader therapeutic approaches beyond vaccines alone
Importance of early intervention with cost-effective treatments
Integration of natural immunity strengthening approaches
Regulatory Considerations
Need to reevaluate approval processes for repurposed medications
Importance of considering cost-effectiveness in treatment protocols
Value of maintaining multiple therapeutic options for future pandemics
VitaminDWiki – COVID-19 treated by Vitamin D - studies, reports, videos
{include}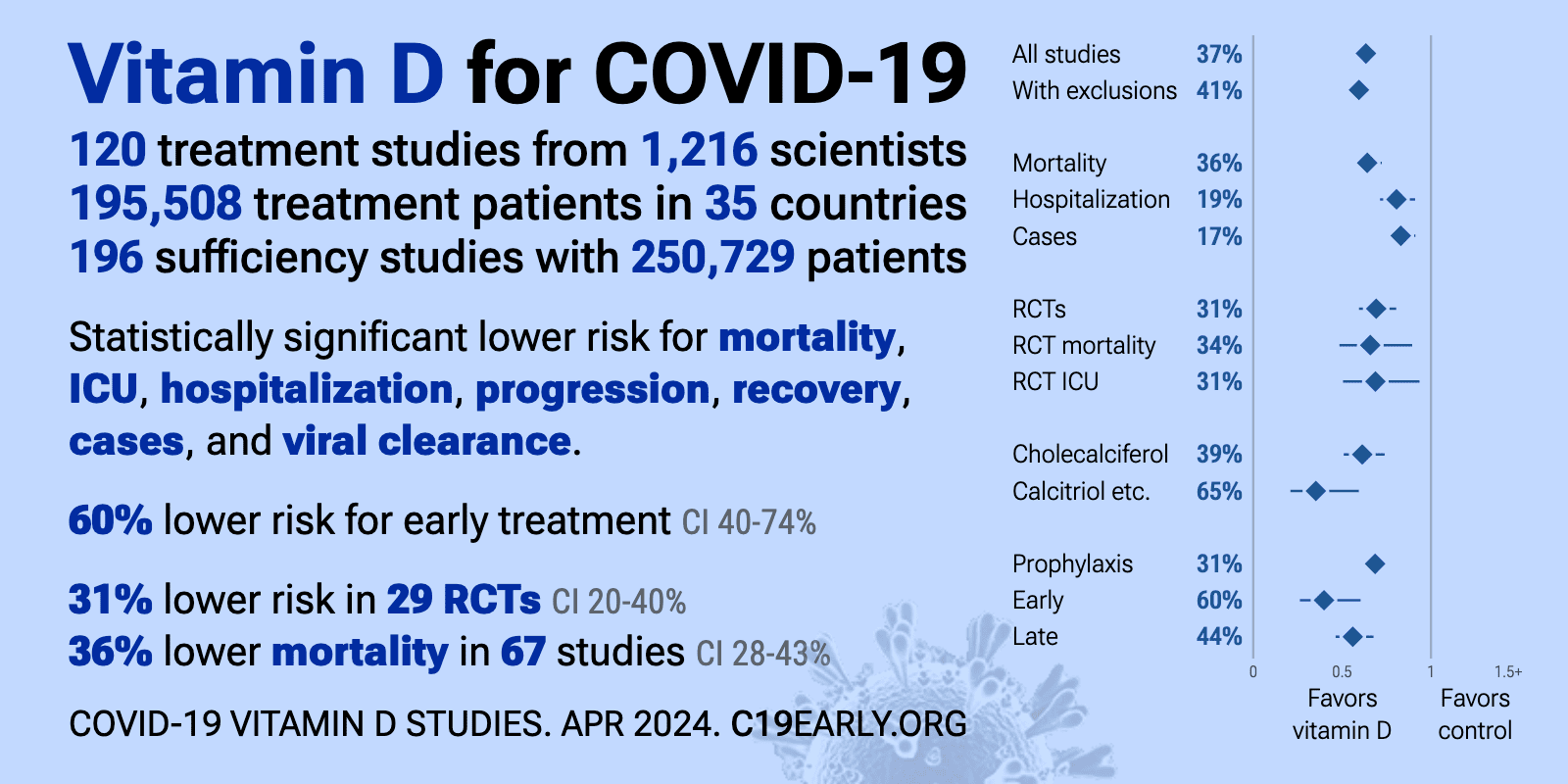
- The above image is automatically updated
10+ VitaminDWiki pages have SUNIL in the title
The list is automatically updated
{LIST()}
VitaminDWiki - Vitamin D can inhibit enveloped virus (e.g. Corona, Herpes, Bird Flu, Epstein, Hepatitis, RSV, etc.) – March 2011
{include}
VitaminDWiki – Flu contains
{include}
VitaminDWiki – Monkeypox and Vitamin D - several studies
VitaminDWiki – Bird flu possible pandemic (Vitamin D can prevent it)- many studies
VitaminDWiki – Respiratory viral infection (RSV) and low vitamin D - many studies
VitaminDWiki – Loading Dose of Vitamin D category contains:
{include}
FLCCC EARLY COVID Vitamin D loading doses (Sunil)
FLCCC = Front Line COVID-19 Critical Care Alliance
Table 3. A Single-Dose Regimen of Calcifediol to Rapidly Raise Serum 25(OH)D above50 ng/mL
| **Body Weight | ||||
| (lbs)** | **Body Weight | |||
| (kgs)** | **Calcifediol | |||
| (mg)** | **Equivalent | |||
| in IU** | **If Calcifediol is not available | |||
| a bolus of Vitamin D3** | ||||
| 15-21 | 7-10 | 0.1 | 16,000 | 20,000 |
| 22-30 | 10-14 | 0.15 | 24,000 | 35,000 |
| 31-40 | 15-18 | 0.2 | 32,000 | 50,000 |
| 41-50 | 19-23 | 0.3 | 48,000 | 60,000 |
| 61-70 | 28-32 | 0.5 | 80,000 | 100,000 |
| 71-86 | 33-39 | 0.6 | 96,000 | 150,000 |
| 86-100 | 40-45 | 0.7 | 112,000 | 200,000 |
| 101-150 | 46-68 | 0.8 | 128,000 | 250,000 |
| 151-200 | 69-90 | 1.0 | 160,000 | 300,000 |
| 201-300 | 91-136 | 1.15 | 240,000 | 400,000 |
| >300 | >137 | 2.0 | 320,000 | 500,000 |
VitaminDWiki – Immunity category contains
{include}
VitaminDWiki - studies in both categories of Immunity and Virus
This list is automatically updated
{category}
