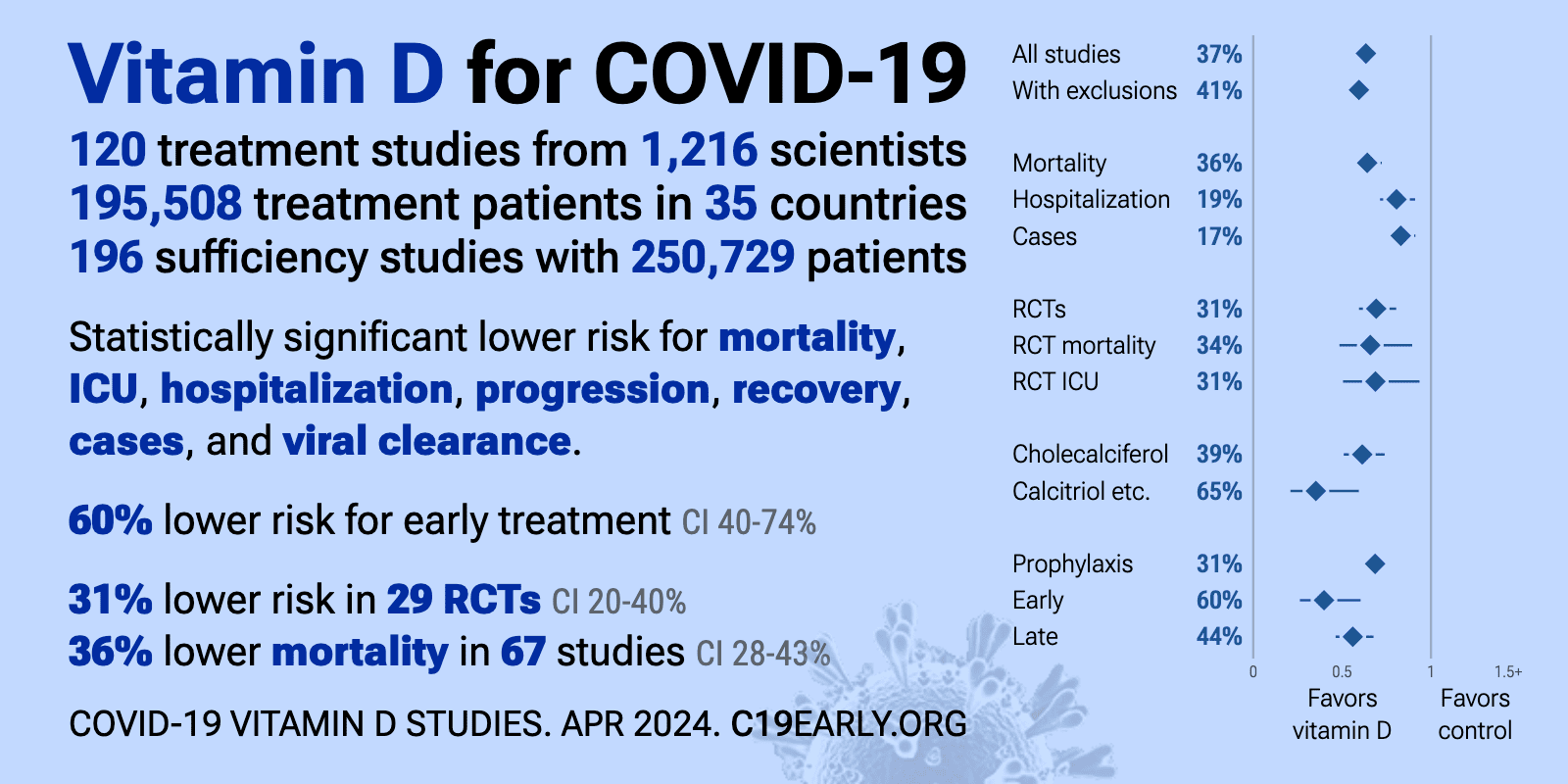
4X less likely to get COVID following 4,000 IU daily for a month – RCT
Efficacy and Safety of Vitamin D Supplementation to Prevent COVID-19 in Frontline Healthcare Workers. A Randomized Clinical Trial
Archives of Medical Research, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arcmed.2022.04.003
Miguel A Villasis-Keever, Mardia G López-Alarcón , Guadalupe Miranda-Nóvales , Jessie N Zurita-Cruz , Aly S Barrada-Vazquez , Joaquín Gonzalez-Ibarra , Monserrat Martínez-Reyes , Concepción Grajales-Muniz , Clara E Santacruz-Tinoco , Bernardo Martínez-Miguel, Jorge Maldonado-Hernandez , Yazm ín Cifuentes-Gonzalez , Miguel Klunder-Klunder, Juan Garduno-Espinosa , Briseida Lopez-Mart í nez , Israel Parra-Ortega
Response to 4,000 IU daily for a month

Outcome

Background
. Associations between vitamin D (VD) deficiency and the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection have been documented in cross-sectional population studies. Intervention studies in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19 have failed to consistently document a beneficial effect.
Objective
. To determine the efficacy and safety of VD-supplementation in the prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection in highly exposed individuals.
Methods
. A double-blind, parallel, randomized trial was conducted. Frontline healthcare workers from four hospitals in Mexico City , who tested negative for SARS-CoV-2 infection, were enrolled between July 15 and December 30, 2020 . Participants were randomly assigned to receive 4,000 IU VD (VDG) or placebo (PG) daily for 30 d.
RT-PCR tests were taken at baseline and repeated if COVID-19 manifestations appeared during follow-up. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 and antibody tests were measured at baseline and at day 45. Per-protocol and intention-to-treat analysis were conducted.
Results
. Of 321 recruited subjects, 94 VDG and 98 PG completed follow-up. SARS-CoV-2 infection rate was lower in VDG than in PG (6.4 vs. 24.5%, p <0.001).
The risk of acquiring SARS-CoV-2 infection was lower in the VDG than in the PG ( RR: 0.23 ; 95% CI: 0.09–0.55) and was associated with an increment in serum levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 (RR: 0.87; 95% CI: 0.82–0.93), independently of VD deficiency. No significant adverse events were identified.
Conclusions
. Our results suggest that VD-supplementation in highly exposed individuals prevents SARS-CoV-2 infection without serious AEs and regardless of VD status.
📄 Download the PDF from VitaminDWiki
8.8 ng/mL increase in median Vitamin D levels after 1 month of 4,000 IU daily
Only one adverse event was statistically significant
| Adverse advent | Supplemented | Placebo | p |
| Headache | 5.3% | 11.8% | 0.044 |
Note: Vitamin D is well known to decrease headaches
thanks to Gustavo Bellini for point this out
VitaminDWiki - Items in both categories Virus and Intervention ( items)
This list is automatically updated
{category}
VitaminDWiki – COVID-19 treated by Vitamin D - studies, reports, videos
{include}
- The above image is automatically updated
