21 fewer days in hospital with ARDS (COVID) if 10,000 IU of Vitamin D daily after enter hospital – RCT April, 2022
Changes in the immune response against SARS-CoV-2 in individuals with severe COVID-19 treated with high dose of vitamin D
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112965
Montserrat Torres, Guiomar Casado, Lorena Vigón, Sara Rodríguez-Mora, Elena Mateos, Fernando Ramos-Martín, Daniel López-Wolf, José Sanz-Moreno, Pablo Ryan-Murua, María Luisa Taboada-Martínez, María Rosa López-Huertas, Miguel Cervero, Mayte Coiras – Multidisciplinary Group of Study of COVID-19 (MGS-COVID)1 Madrid
Highlights
Treatment with 10,000 IU/day of cholecalciferol was safe during severe COVID-19.
Anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 was significantly increased in 10,000 IU/day group.
Individuals who received 10,000 IU/day of cholecalciferol showed increased CD4 count.
Individuals with ARDS in 10,000 IU/day group stayed at the hospital less time.
The 10,000 IU/day group showed increased antiviral cytotoxic activity.


Main cause of severe illness and death in COVID-19 patients appears to be an excessive but ineffectual inflammatory immune response that may cause severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Vitamin D may favour an anti-inflammatory environment and improve cytotoxic response against some infectious diseases. A multicenter, single-blind, prospective, randomized clinical trial was approved in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) of 14.8 ng/mL (SD: 6.18) to test antiviral efficacy, tolerance and safety of 10,000 IU/day of cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) for 14 days, in comparison with 2,000 IU/day.
After supplementation, mean serum 25(OH)D levels increased to
19 ng/mL on average in 2,000 IU/day versus
29 ng/mL in 10,000 IU/day group (p <0.0001).
Although levels of inflammatory cytokines were not modified by treatment with 10,000 IU/day, there was an increase of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 and higher levels of CD4+ T cells, with predominance of T central memory subpopulation.
Cytotoxic response against pseudotyped SARS-CoV-2 infected cells was increased more than 4-fold in patients who received 10,000 IU/day . Moreover, levels of IFN? were significantly higher in this group.
Beneficial effect of supplementation with 10,000 IU/day was also observed in participants who developed ARDS and stayed at the hospital for 8.0 days , whereas those who received 2,000 IU/day stayed for 29.2 days (p=0.0381). Administration of high doses of vitamin D3 as adjuvant of the standard care treatment during hospitalization for COVID-19 may improve the inflammatory environment and cytotoxic response against pseudotyped SARS-CoV-2 infected cells, shortening the hospital stay and, possibly, improving the prognosis.
📄 Download the PDF from VitaminDWiki
Graphical summary

Clipped from PDF
The inclusion criteria for the participants in the study were being adults (>18 years old) hospitalized for at least seven days from the onset of COVID-19 symptoms, which is when usually began the inflammatory phase, with a diagnosis of pneumonia due to COVID-19
Speculation:
No hospitalization if had gotten high dose vitamin D at COVID symptom onset
VitaminDWiki: Take lots of Vitamin D at first signs of COVID
thanks to Gustavo Bellini for pointing out this study
VitaminDWiki- Items in both categories Virus and Intervention ( items)
This list is automatically updated
{category}
VitaminDWiki – COVID-19 treated by Vitamin D - studies, reports, videos
{include}
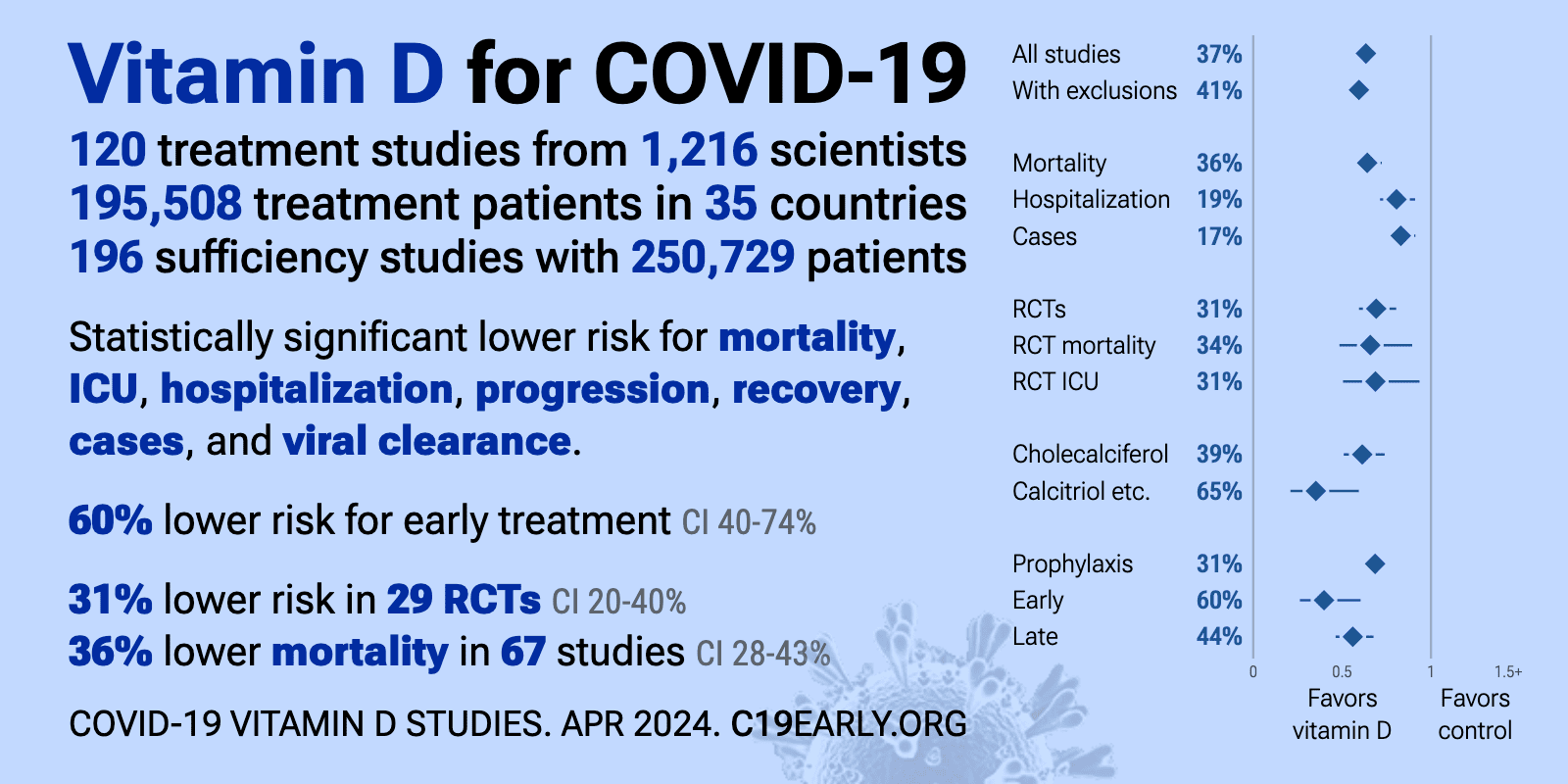
- The above image is automatically updated
VitaminDWiki pages with HIGH-DOSE in title (63 as of April 2022)
This list is automatically updated
{LIST()}
